6. Sales and marketing
Objetives
- For students to learn vocabulary and expressions about advertising, sales and job interviews.
- For students to learn how to basically advertise a product, a business or a job as well as how to apply for a job interview.
6.1. Advertising
Advertising is an activity intended to sell a product or a service and, sometimes, it tries to change people’s ideas about something. Advertising appears almost everywhere telling people about a product or a service and trying to make people want to buy that product or service.
In advertising contexts, language is a powerful tool to influence people. The language chosen to convey specific messages with the intention of influencing their behavior is key in these contexts. But also both visual content and design have a strong impact on the consumer because they help to identify a product or service and remember it.

Figure 33 shows the advertisement of Wrangler jeans
For advertising, it is very important to understand the connotation of words, that is, the feelings and ideas that are suggested by words, rather than the actual meaning provided by the dictionary. It is then relevant to consider that the audience also provides their own meaning into the language used in advertising.
Repetition is one of the most frequent techniques used in advertising. Advertisements often use slogans that are repeated over and over again so as people remember them. Sometimes they use a famous person talking about a product or a service, and sometimes they compare a product with another one of the same type. N
- Analyze the language used by these advertisements.
EAudiovisual
6.2. Sales
For any successful business growth, a carefully developed combination of sales and marketing plan is key. While "selling" consists of interpersonal interaction such as meetings, telephone calls and networking where business people engage in with prospects and customers, "marketing" encompasses programs used by businesses to reach and persuade prospects which include advertising, public relations, direct mail and more.
So, to build a successful business, a program combining sales and marketing which leads prospects through all the sale cycle must be developed, referring to the sale cycle as the course of time between the initial contact made with a customer, the identification of services or goods to be procured, the acceptance of the intended purchase, and the transaction that completes the sale. N
Here is a list with vocabulary related to sales:
Word |
Meaning |
|
after sales service |
Service that continues after the sale of a product (maintenance, etc.) |
|
agent |
Person or company that acts for another and provides a specified service. |
|
B2B e-commerce |
Business to business e-commerce: use of commercial networks, online product catalogues and other online resources to obtain better prices and reach new customers. |
|
B2C e-commerce |
Business to consumer e-commerce:
|
|
benchmarking |
Comparing one's products to those of competitors in order to improve quality and performance. |
|
buyer |
1) Any person who makes a purchase.
|
|
cash refund offer |
Offer to pay back part of the purchase price of a product to customers who send a "proof of purchase" to the manufacturer. |
|
chain store |
Two or more shops or outlets that have the same owners and sell similar lines of merchandise. |
|
client |
A person who buys services or advice from a lawyer, an accountant or other professional. |
|
close |
Finalize a sale or deal. |
|
convenience store |
Small shop located near a residential area that opens long hours, seven days a week. |
|
coupon |
Certificate that gives customers a saving when they purchase a specific product. |
|
deal |
A business transaction. |
|
department store |
A large shop or store that carries a wide variety of product lines. |
|
direct investment |
Entering a foreign market by setting up assembly or manufacturing facilities in that country. |
|
discount |
A reduction in price. |
|
e-commerce |
Buying and selling by electronic means, primarily on the internet. |
|
e-marketing |
Promotion of products and services over the internet. |
|
extranet |
Network that connects a company with its suppliers and distributors |
|
follow-up |
Maintain contact after the sale to ensure customer satisfaction. |
|
franchise |
Association between a manufacturer or wholesaler (franchiser) and an independent business person (franchisee) who buys the right to own and operate a unit in the franchise system. |
|
guarantee |
A promise that product will be repaired or replaced if faulty. |
|
intranet |
A network that connects people to each other within a company. |
|
joint venture |
A way of entering a foreign market by joining with a foreign company to manufacture or market a product or service. |
|
market leader |
The company with the largest market share in an industry. |
|
mark up |
Percentage of the price added to the cost to reach a selling price. |
|
opinion leader |
Person with a reference, who, because of competence, knowledge, or other characteristics, exerts influence on others. |
|
packaging |
Designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product. |
|
product line |
A group of products that are closely related. |
|
prospect |
A potential customer. |
|
representative |
A person who represents and sells for a company. |
|
retail |
To sell in small quantities, as in a shop, directly to customers. |
|
shopping centre |
Group of shops developed and managed as a unit. |
|
telephone marketing |
Using the telephone to sell directly to customers. |
|
trade fair |
An exhibition at which companies in a specific industry can show or demonstrate their products. |
|
viral marketing |
The internet version of word-of-mouth marketing - email messages that customers pass on to friends. |
|
wholesale |
To sell goods and services to those buying for resale (e.g. a shop) or for business use. N |
-
Analyze this set of videos about sales strategies:
EAudiovisual
6.3. Resume
The resume is a very important tool to be accepted for an interview. An effective resume presents people in a way that convinces the employer that they have what it takes to be successful in the position or career they are advertising.
A resume which is pleasing to the eye makes the receiver want to read it. It stimulates interest in meeting its owner and learning more about him or her. It inspires the prospective employer to ask the person to come in for an interview.
A resume should be useful to pass the employer’s selection process (requisite educational level, number years’ experience, etc.) by providing basic facts which might favorably influence the employer.
When the resume is appropriately written, clear, well-organized, and well-designed, it will present its owner as a professional person with high standards and excellent writing skills. N

Figure 34 shows a model resume form
- Study these pieces of advice on how to write a resume.
EAudiovisual
Here are some interesting links where you can learn a lot about resume writing:
6.4. Job interview
Preparation for an interview is essential. It is a good piece of advice to prepare and practice giving responses to the questions before the interview.
It is also advisable to find out as much information as possible about the company as well as the position the applicant is interested in. And finally, it is very important to remember to take an extra copy of the CV/résumé so that the employer can refer to it.
The list of questions below is intended to be used as a guide when attending a job interview.
|
Tell me about yourself. |
|
How would you describe yourself? (character / personality) |
|
Are you married? Single? Do you have a partner? |
|
What are your strengths / weaknesses? |
|
What do you do in your free time?
|
|
Why are you interested in working for our company?
|
|
What type of position do you think you are suited for / would suit you? |
|
How would you describe the position we have to offer? |
|
What aspects of the position are you most / least interested in? |
|
What would you like to find in this job that you didn't have in your previous job? |
|
How do you think you could develop the position?
|
|
What have you got to offer us?
|
|
What do you think you gained by working in your last job? |
|
What were you responsible for?
|
|
What do you think of your (last) boss? |
|
Why do you want to leave your present job?
|
|
What are your salary requirements?
|
|
Have you received any offers for a job? |
|
Why have you had to look for a job for so long?
|
|
How do you feel about your future in the profession? |
|
Have you had any failures? What failures have you had?
|
|
What sort of obstacles have you come across / encountered in your work? |
|
If you had to recruit colleagues, what qualities would you look for? |
|
Would you be willing to relocate/to move to another part of the country/to work abroad? |
|
Don't you think you have too much experience / you are over-qualified for this job? |
|
How long do you think you would stay with us?
|
|
Which do you prefer: to work alone or in a team?
|
|
Do you know how to manage a team?
|
|
Why should I recruit you?
|
|
Do you have any comments to make, or any questions to ask? |
Here are some videos about job interviews:
Here you have important idioms to learn about jobs and employment which may be used in job interviews
- Here are some exercises to practice talking about sales:
6.5. Past simple regular and irregular verbs
Simple past tense is used to refer to states in the past or actions which started and finished in the past; to retell stories and for the second conditional.
Past Simple Tense of the verb 'be'
|
AFFIRMATIVE |
NEGATIVE |
|
I was a secretary. |
I was not (wasn't) a secretary. |
|
You were a boss. |
You were not (weren't) a boss. |
|
He was at the reception |
He was not (wasn't) at reception. |
|
She was late for work. |
She was not (wasn't) late for work. |
|
It was a good product. |
It was not (wasn't) a good product. |
|
We were at the office. |
We were not (weren't) at the office. |
|
They were in a meeting. |
They were not (weren't) in a meeting. |
- Now do these exercises to practice the past simple of the verb “be” affirmative and negative
|
'Yes / No' Questions with 'Be' |
'Wh' Questions with 'Be' |
|
Was I aware the risks? |
Why was I so careless? |
|
Were you late? |
Where were you? |
|
Was he at the factory? |
When was he at the office? |
|
Was she a good worker? |
How was she? |
|
Was it a new product? |
How was it? |
|
Were we right? |
Why were we wrong? |
|
Were they at work? |
When were they at work? |
- Now try these exercises:
WWeb
Questions:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-2.html
Affirmative, negative and questions:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-3.html
The past simple tense (simple past) with other verbs
|
Affirmative with other verbs |
Negative |
|
I worked all night. (regular) |
I did not (didn't) work. |
|
You played tennis. (regular) |
You did not (didn't) play tennis. |
|
He cooked pizza. (regular) |
He did not (didn't) cook pizza. |
|
She listened to the boss. (regular) |
She did not (didn't) listen to the boss. |
|
It rained a lot. (regular) |
It did not (didn't) rain. |
|
We ate caviar. (irregular) |
We did not (didn't) eat caviar. |
|
They drank tea. (irregular) |
They did not (didn't) drink tea. |
The affirmative of the past tense of regular verbs is formed by adding '-ed' to the infinitive. For example, 'work' becomes 'worked'. However, there are some irregular verbs for example 'go' becomes 'went' and 'run' becomes 'ran'.
How to pronounce the past of regular verbs:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/how-to-pronounce-ed.html
List of irregular verbs:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/support-files/50_common_irregular...
Video and explanation about past tense:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/irregular-verbs.html
- Now try these exercises about past irregular verbs
Here are the 'yes / no' questions and wh-questions
|
'Yes / No' Questions |
'Wh' Questions |
|
Did I walk? |
Where did I go? |
|
Did you play? |
What did you play? |
|
Did he cook? |
What did he cook? |
|
Did she listen? |
Why did she listen? |
|
Did it rain? |
When did it rain? |
|
Did we eat? |
Where did we eat? |
|
Did they travel? |
How did they travel? |
- Now try these exercises:
Yes/no questions:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-5.html
Wh- questions:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-6.html
- Here are some mixed exercises for the simple past.
N
Exercise 1:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-7.html
Exercise 2:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-8.html
Exercise 3:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-9.html
Exercise 4:
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/past-simple-exercise-10.html
- Watch these videos to review the past tense for regular and irregular
verbs.
EAudiovisual
6.6. Time expressions
Time expressions are used to specify when something happened, happens or will happen.
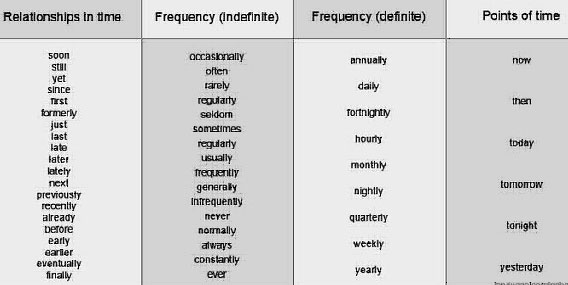
Figure 35 shows a list of time expressions
|
Common Past Time Expressions |
Example Sentences |
Similar Expressions |
|
yesterday
|
I walked to work yesterday. Yesterday, I walked to work. |
yesterday morning
|
|
the day before yesterday
|
Redd bought a car the day before yesterday. The day before yesterday, Redd bought a car. |
the week before last (week)
|
|
last night
|
Avril travelled to Halifax last night. Last night, Avril travelled to Halifax. |
last time
|
|
this morning
|
Kathleen called me this morning. This morning, Kathleen called me. |
this afternoon
|
|
one week ago
|
Kenneth and his wife had a baby one week ago. One week ago, Kenneth and his wife had a baby. |
one hour ago
|
|
in 1990
|
Darren finished university in 1990. In 1990, Darren finished university. |
in 1970
|
|
when + subject + past tense verb
|
Paul played basketball when he was a student. When he was a student, Paul played basketball. |
when I was born when John finished high school when I turned 18 N |
Here is a webpage with time expressions and how they are pronounced.
6.7. Present perfect
The present perfect tense is very important to provide formality to the discourse turning it appropriate for business contexts.
The present perfect tense is formed using the affirmative or negative present tense of the verb “to have”: 'have' / 'has' / 'haven't' / 'hasn't' + the past participle of the main verb.
|
Affirmative |
Negative |
|
I have (I've) played |
I have not ( haven't) eaten breakfast today |
|
You have (You've) worked |
You have not (haven't) been to Asia |
|
He has (He’s) written |
He has not (hasn't) seen the new film |
|
She has (She’s) walked |
She has not (hasn't) played tennis |
|
It has (It’s) rained |
It has not (hasn't) snowed this winter |
|
We have (We’ve) travelled |
We have not (haven't) slept all night |
|
They have (They’ve) studied |
They have not (haven't) tried the food |
- Now do the following exercises:
|
'Yes / No' Questions |
'Wh' Questions |
|
Have I missed the bus? |
Where have I left my briefcase? |
|
Have you visited London? |
What have you done today? |
|
Has he worked as a waiter before? |
Why has the boss gone already? |
|
Has she met the manager? |
Where has she been in the UK? |
|
Has it been cold this week? |
Why has it rained so much this summer? |
|
Have we arrived too early? |
What have we done? |
|
Have they studied management before? |
Where have they learned marketing? |
- Now try these exercises: N
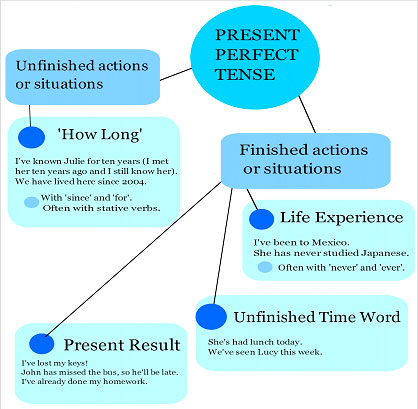
Figure 36 shows the uses of the present perfect tense
The present perfect tense is used for unfinished and finished actions:
Unfinished actions:
The present perfect tense is used when talking about unfinished actions
that started in the past and continue to the present. Usually it is used
to say 'how long' an action or state has continued adding 'since' and 'for'.
Often, stative verbs are used in this situation.
Examples:
'Since' and 'For'
'Since' is used with a fixed time in the past (2004, April 23rd, last
year, two hours ago). The fixed time can be another action, indicated with
the past simple (since I was at school, since I arrived).
Examples:
'For' is used with a period of time (2 hours, three years, six months):
Finished Actions
For life experience it is not mentioned when the experience happened,
just sometime in the past.
Examples:
For a finished action with a result in the present, focusing on the result.
Examples:
Use present perfect with an unfinished time word (this month, this week,
today, in the last year).
Examples:
- I've been to Paris (in my life, but now I'm in London, where I live).
- She has been to school today (but now she's back at home).
- They have never been to California.
- 'Where's John?' 'He's gone to the shops' (he's at the shops now).
- Julie has gone to Mexico (now she's in Mexico).
- They've gone to Japan for three weeks (now they're in Japan). N
Participles 'Been' and 'Gone'
In this tense, both 'been' and 'gone' are used as the past participle of 'go', but in slightly different circumstances.
Been
'Been' is used (often when talking about 'life experience') to mean that the person being talked about has visited the place, and come back. And the preposition 'to' is used before the venue:
Gone
'Gone' is used (often when talking about an action with a result in the present) to mean that the person is at the place now:

